

INSTRUMENTS
- High resistance voltmeter.
- 2 Cu/CuSO4 electrodes.
- Trailing conductor reel and mounting.
METHOD
4.1.1. Use Procedure 2 to establish remote reference electrode.
4.1.2. Turn the cathodic protection installation to its normal operating mode.(on)
4.2.1. Connect the fixed, reference electrode to the positive pole of the high resistance voltmeter in such a way that this half-cell is immobile during the survey.
4.2.2. Connect the roving electrode to the negative pole of the high resistance voltmeter.
4.2.3. Unreel the conductor to the required starting position of the overline survey and again secure. The trailing conductor should then be free to play out as the survey progresses.
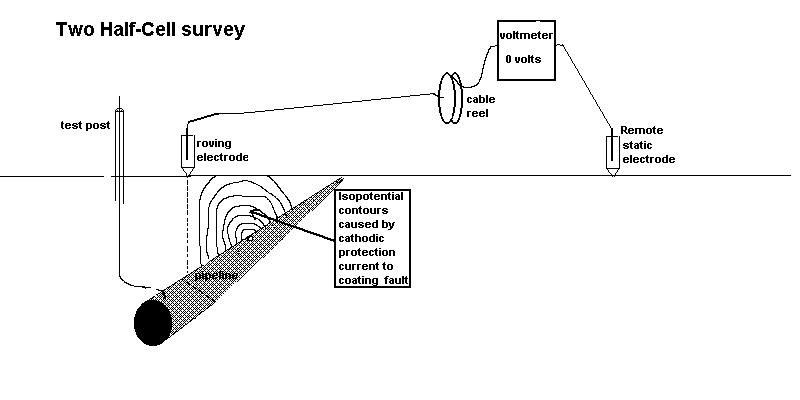
4.3.1. Contact the ground with the roving electrode, at one meter intervals along the path of the pipeline, noting the voltage readings between the electrodes, at each step.4.3.2. The locations of highest voltage should be marked.
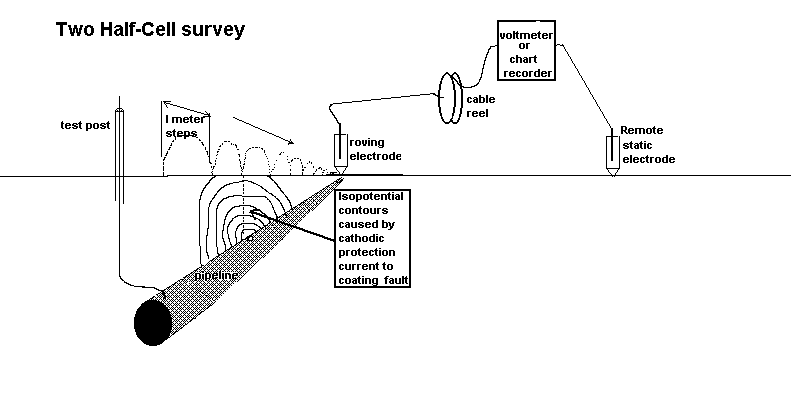
4.4.1 When the required section of pipeline has been surveyed, the roving electrode should be stepped across the pipeline route at the locations of highest voltage.
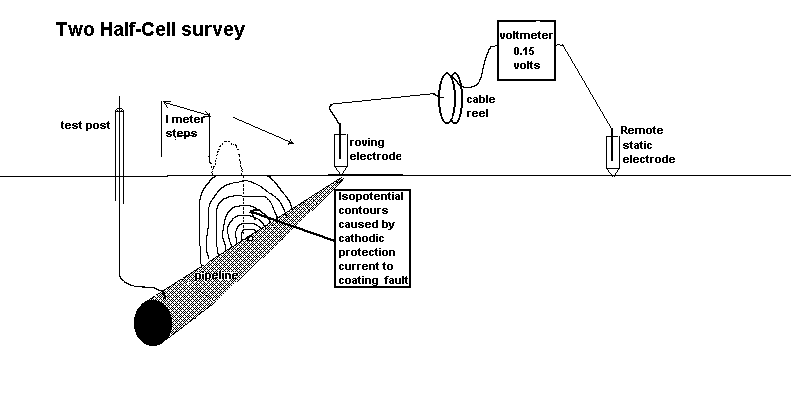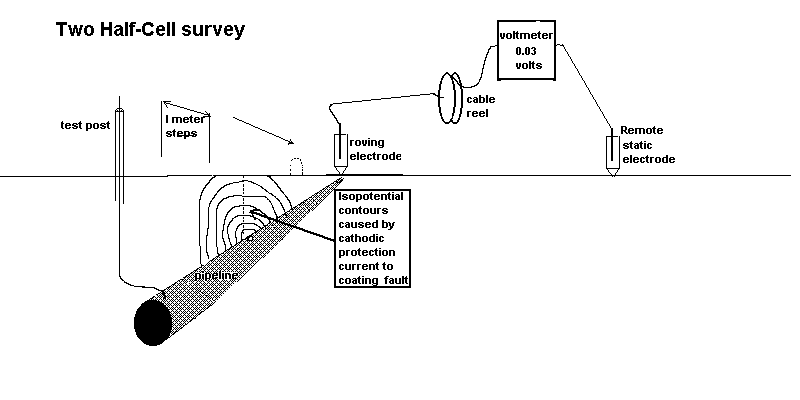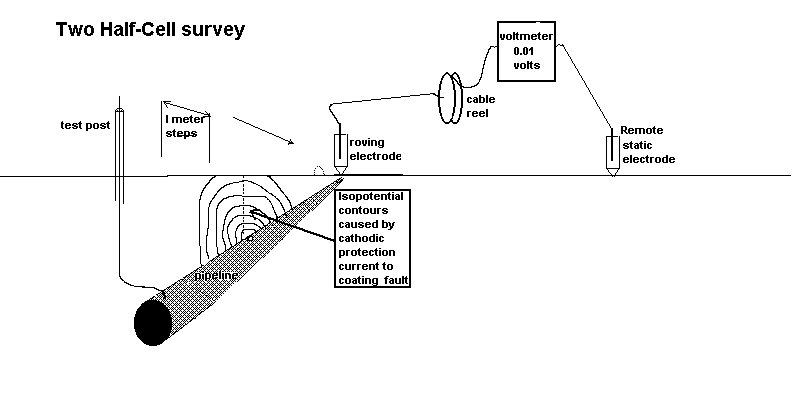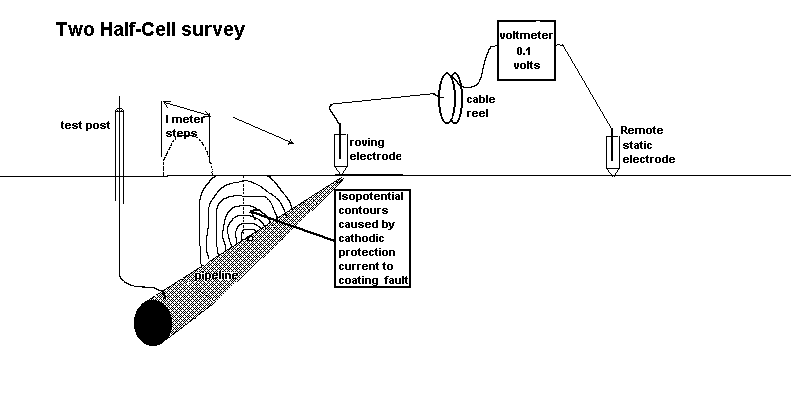
4.4.2. These 'transverse' readings should extend as far as possible, or from "remote earth" to "remote earth".
INTERPRETATION
The largest voltages are obtained where the IR drop in the soil is caused by the CP current returning to the pipeline. It follows that the marked locations are over coating faults which allow contact between the backfill and the pipe metal.
It has been found that transverse readings can indicate the severity of the coating fault and help to eliminate errors caused by other IR drops.
click to return to front page